Rabu, 7 Disember 2011
Mother board
The motherboard is the main component inside the case. It is a large rectangular board with integrated circuitry that connects the other parts of the computer including the CPU, the RAM, the disk drives (CD, DVD, hard disk, or any others) as well as any peripherals connected via the ports or the expansion slots.Components directly attached to the motherboard include:
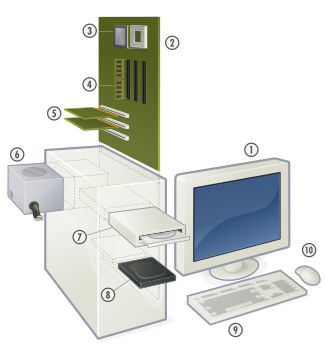
Hardware of a modern personal computer
1. Monitor
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM
5. Expansion cards
6. Power supply
7. Optical disc drive
8. Hard disk drive
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM
5. Expansion cards
6. Power supply
7. Optical disc drive
8. Hard disk drive
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
Selasa, 6 Disember 2011
Read-only memory
Read-only memory (or simple ROM) is a type of computer memory. Unlike RAM, it keeps its contents even when the computer or device is turned off. Usually, ROM cannot be written to when the computer runs normally. ROM is used for important programs like the BIOS which tells the computer how to start, or the firmware of certain devices, which usually does not need to be modified. Usually, ROM comes on computer chips.
There are different kinds of ROMs:
- Masked ROM
: This kind is written once, at the factory. It cannot be changed at all later on. Its main benefit is that it is very cheap to make.
- PROM
: Can be programmed once. Comes unprogrammed from the factory. Programming consists in removing connections. Has been replaced by EPROMs
- EEPROM
: This kind can be erased using an electrical signal. Today, flash memory is often used.
Jumaat, 2 Disember 2011
Jaringan Sejagat (b. Inggeris: World Wide Web), juga dikenali sebagai WWW atau web, ialah sebuah sistem jaringan dokumen hiperteks yang boleh diakses melalui Internet. Seseorang perlu menggunakan pelayar web untuk "meluncuri" Jaringan Sejagat. Dokumen dalam Jaringan Sejagat dikenali sebagai laman web, dan dikumpulkan dalam satu kawasan yang dikenali sebagai tapak web. Sesebuah laman web boleh mengandungi teks, imej, video, dan pautan kepada laman lain. Jaringan Sejagat dicipta oleh Tim Berners-Lee, seorang penyelidik di CERN, pada tahun 1989.
Sejarah teknologi maklumat
Istilah "teknologi maklumat" muncul pada sekitar dekad 1970-an. Bagaimanapun, konsepnya yang asas boleh dikesani jauh lebih lama lagi. Pada sepanjang abad ke-20, pihak tentera telah berikat dengan berbagai-bagai industri untuk membangunkan elektronik, komputer, dan teori maklumat. Secara sejarah, pihak tentera telah mendorong penyelidikan-penyelidikan tersebut dengan memotivasi dan membiayai inovasi dalam bidang penjenteraan dan pengkomputan.
Komputer komersil yang pertama ialah UNIVAC I yang direka bentuk oleh J. Presper Eckert dan John Mauchly untuk Biro Banci Amerika Syarikat. Akhir dekad 1970-an memperlihatkan kebangkitan mikrokomputer, diikuti dengan rapat oleh komputer peribadi IBM pada tahun 1981. Sejak dari masa itu, empat generasi komputer telah berkembang, dengan setiap generasi melambangkan satu langkah yang dicirikan oleh perkakasan yang semakin kecil dan berupaya. Generasi pertama menggunakan tiub vakum, dengan generasi-generasi kedua dan ketiga masing-masing menggunakan transistor dan litar bersepadu. Generasi keempat, iaitu generasi terkini, menggunakan sistem-sistem yang lebih rumit seperti penyepaduan skala sangat besar (VLSI).
Langgan:
Catatan (Atom)